Shrimp and Raspberry Pi run the Morse Twitter Display
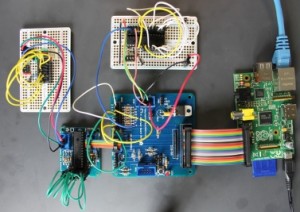
Tworse (the Twitter Morse Code display) is now running on the Shrimp + Pi as well as on an Arduino + Pi.
The Raspberry Pi monitors a twitter stream - in this case, it's looking for tweets with the hashtag #morsetweeter.
It converts each tweet to upper case, removes any non-ascii characters, and sends it over a serial link to the Arduino or Shrimp.
The Shrimp reads lines using the Serial interface and flashes them in Morse Code. It then sends a text version of the Morse-coded line back to the Pi which displays it on the console.
 |
| Running the app on the Pi |
The sketch for the Shrimp and the Python Script for the Pi are now on github.
The sketch is a bit long for a blog post, but here is the Python code on the Pi.
import time from twython import Twython import serial def parse(filename, comment_char='#', separator='='): options = {} with open(filename) as f: for line in f: start = line.split(comment_char)[0] if separator in start: option, value = map(lambda x: x.strip(),start.split(separator, 1)) options[option] = value return options class ArduinoSerial(): def __init__(self): self.ser = serial.Serial('/dev/ttyACM0', 9600) def send(self, text): self.ser.write(self.ascii_only(text)) def receive(self): return self.ser.readline() @staticmethod def ascii_only(text): return ''.join(i for i in text if ord(i)<128) def get_twitter(): ini = parse('secrets/twitter.ini') key = ini['KEY'] secret = ini['SECRET'] tw = Twython(key, secret, oauth_version=2) return Twython(key, access_token=tw.obtain_access_token()) if __name__ == '__main__': arduino = ArduinoSerial() time.sleep(1.0) twitter = get_twitter() tweets = twitter.search(q='#morsetweeter') for status in tweets['statuses']: line = (status['text']).upper()+'\n' print line, arduino.send(line) print arduino.receive(),



Comments
Post a Comment